Keratoconus. It’s a word many people haven’t heard, but for those affected, it’s a significant and often challenging eye condition. This progressive disorder, characterized by the thinning and bulging of the cornea into a cone-like shape, can profoundly impact vision. Understanding what keratoconus is, how it’s diagnosed, and the available treatment options is important for anyone experiencing its symptoms. Early detection is often the key to preserving vision and maintaining a good quality of life.
We’ll educate you on this complex eye disease, shedding light on its symptoms, the diagnostic process, and the range of treatments available today, including both surgical and non-surgical keratoconus treatment approaches.
If you’re in the Los Angeles area and seeking an eye specialist near me, understanding these options can empower you to make informed decisions about your eye health.
What Is Keratoconus?
At its core, keratoconus is a condition where the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped front surface of your eye, progressively thins and bulges outward. Instead of maintaining its smooth, rounded shape, it takes on a more conical form. This distortion fundamentally alters the way light enters your eye, leading to blurry and distorted vision.
Typically, keratoconus begins to manifest in the teenage years or early adulthood, although it can appear later. Its progression varies among individuals; for some, it may stabilize after a few years, while for others, it continues to worsen over time, requiring more intensive eye disease treatment.
Symptoms of Keratoconus
Recognizing the early signs of keratoconus and treatment options can make a significant difference. While symptoms can vary from person to person, common indicators include:
- Blurry or distorted vision: This is often one of the first and most noticeable symptoms.
- Increased sensitivity to light and glare (photophobia): Bright lights can become uncomfortable or even painful.
- Frequent prescription changes in glasses or contacts: Your vision may seem to worsen rapidly, necessitating frequent updates to your corrective lenses.
- Difficulty seeing at night: Glare and halos around lights can make night driving particularly challenging.
- Eye strain and headaches: Your eyes may work harder to compensate for the distorted vision, leading to discomfort.
- Sudden worsening of vision in one or both eyes: This can be a concerning symptom that warrants immediate attention from an eye specialist.
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they are persistent or worsening, it’s vital to consult an eye specialist to determine how keratoconus is diagnosed and treated.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of keratoconus isn’t fully understood, several factors are believed to play a role:
- Genetic predisposition (family history): If a close family member has keratoconus, your risk may be higher.
- Chronic eye rubbing: Persistent and vigorous eye rubbing is a significant risk factor and can accelerate the progression of the condition.
- Certain medical conditions: Keratoconus has been linked to conditions such as Down syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, and other connective tissue disorders.
- Environmental and hormonal influences: While less defined, these factors are also thought to contribute.
Also Read: How to Tell If You Have Keratoconus vs. Astigmatism
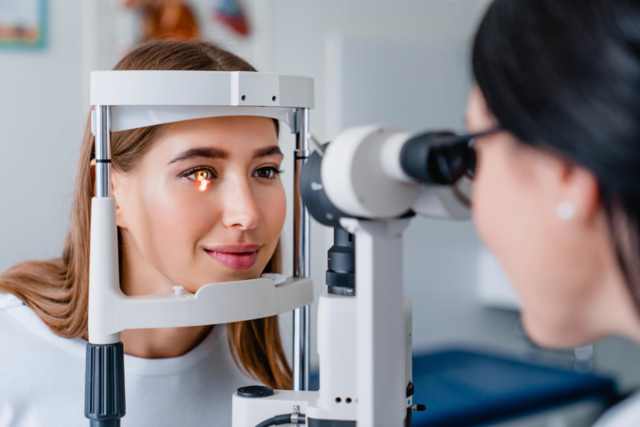
How Keratoconus Is Diagnosed
Accurate diagnosis is the first step in effective keratoconus treatment and vision correction. An eye specialist will typically perform a comprehensive eye exam, which may include:
- Corneal topography: This advanced imaging technique creates a detailed map of the curvature and shape of your cornea, revealing any irregularities indicative of keratoconus. This is a cornerstone of keratoconus diagnosis.
- Pachymetry: This measures the thickness of your cornea. As keratoconus progresses, the cornea thins.
- Slit-lamp exam: Using a specialized microscope, the doctor can closely examine the structure of your cornea for signs of thinning, scarring, or conical protrusion.
These diagnostic tools allow your eye specialist to confirm the presence of keratoconus and assess its severity, guiding the appropriate keratoconus care plan.
Treatment Options for Keratoconus
The good news is that significant advancements have been made in keratoconus treatment, offering a range of options depending on the stage and severity of the condition.
Eyeglasses or Soft Contact Lenses (Early Stages)
In the very early stages of keratoconus, when vision distortion is mild, regular eyeglasses or soft contact lenses may be sufficient to correct vision. However, as the cornea becomes more irregular, these traditional corrective lenses often cease to provide adequate vision correction.
Eyeglasses or Soft Contact Lenses (Early Stages)
In the very early stages of keratoconus, when vision distortion is mild, regular eyeglasses or soft contact lenses may be sufficient to correct vision. However, as the cornea becomes more irregular, these traditional corrective lenses often cease to provide adequate vision correction.
Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) or Scleral Lenses
For many individuals with keratoconus, especially as the condition progresses, specialized contact lenses are the primary form of vision correction.
- Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) lenses: These hard lenses maintain a consistent shape, effectively creating a new, smooth optical surface over the irregular cornea. They can significantly improve vision by masking the corneal irregularities.
- Scleral lenses: These large-diameter RGP lenses vault over the entire cornea and rest on the white part of the eye (sclera). This design creates a fluid-filled reservoir between the lens and the cornea, providing exceptional comfort and clear vision, especially for more advanced cases or those who can’t tolerate traditional RGPs. These are considered a non-surgical keratoconus treatment option.
Corneal Cross-Linking (CXL)
Corneal cross-linking is a revolutionary, minimally invasive procedure designed to strengthen the corneal tissue and slow or even halt the progression of keratoconus. During CXL, custom-made riboflavin eye drops are applied to the cornea, followed by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. This process creates new bonds between collagen fibers in the cornea, making it stiffer and more resistant to further bulging. CXL is a critical intervention, especially in cases of progressive keratoconus.
Intacs or Corneal Implants
Intacs are small, clear, arc-shaped inserts surgically placed within the cornea to help flatten its conical shape. They are often used in moderate keratoconus when contact lenses no longer provide sufficient vision correction. Intacs can improve vision and sometimes make it easier to wear contact lenses.
Corneal Transplant (Advanced Stages)
In severe cases of keratoconus, particularly when there is significant corneal scarring, extreme thinning, or when other treatments have failed, a corneal transplant may be necessary. This procedure involves replacing the diseased cornea with a healthy donor cornea. While it’s a more invasive surgical option, corneal transplants for keratoconus have a high success rate, though recovery can be longer.
Living with Keratoconus
Living with keratoconus requires ongoing attention and care. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with your eye specialist are important to track the progression of the condition and adjust your treatment plan as needed. It’s also vital to avoid chronic eye rubbing, as this can worsen the condition. Vision rehabilitation and support groups can also be beneficial, providing resources and a sense of community for those navigating life with keratoconus.
Conclusion
Keratoconus, while a serious eye condition, is increasingly manageable with early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. The advancements in corneal treatments and specialty lenses offer significant hope for clearer vision and a better quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
If you suspect you have keratoconus or are experiencing any of the symptoms discussed, do not hesitate to consult with Soroudi Advanced LASIK & Eye Centers for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized care plan.
If you suspect you have keratoconus or are experiencing any of the symptoms discussed, do not hesitate to consult with Soroudi Advanced LASIK & Eye Centers for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized care plan.